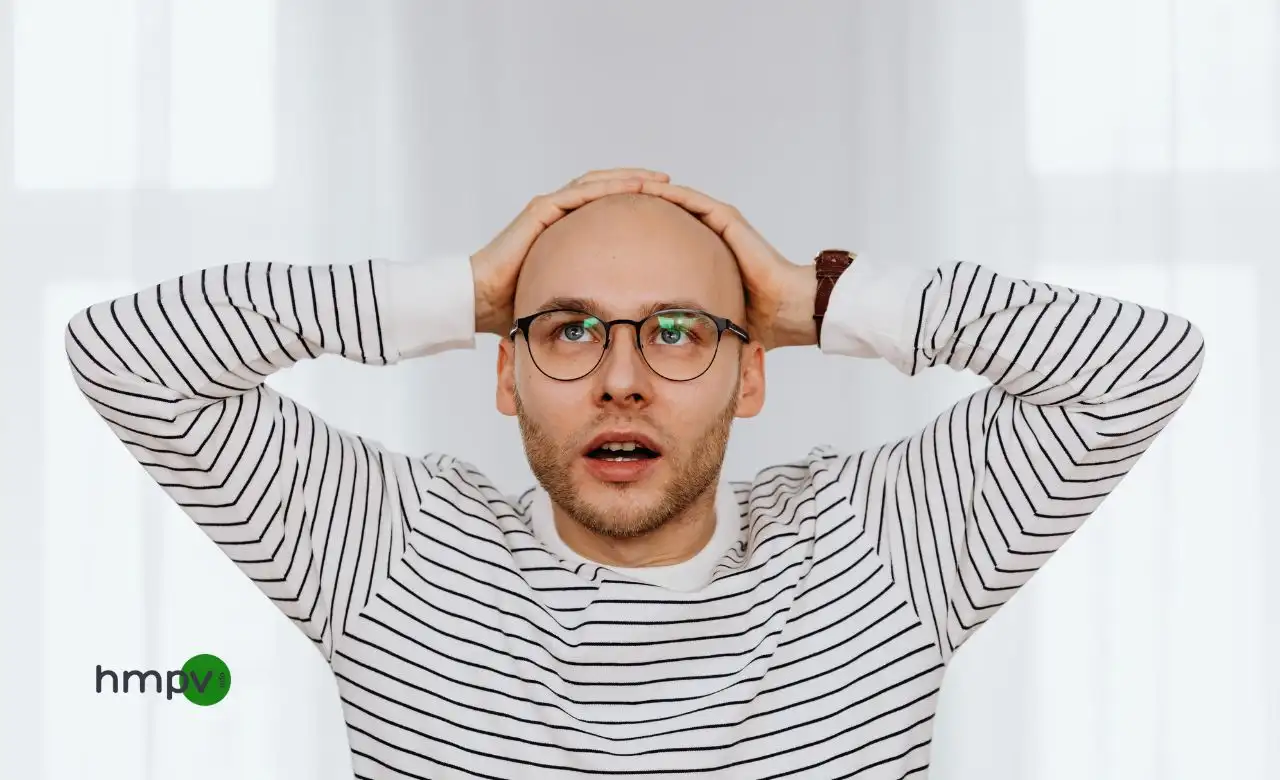
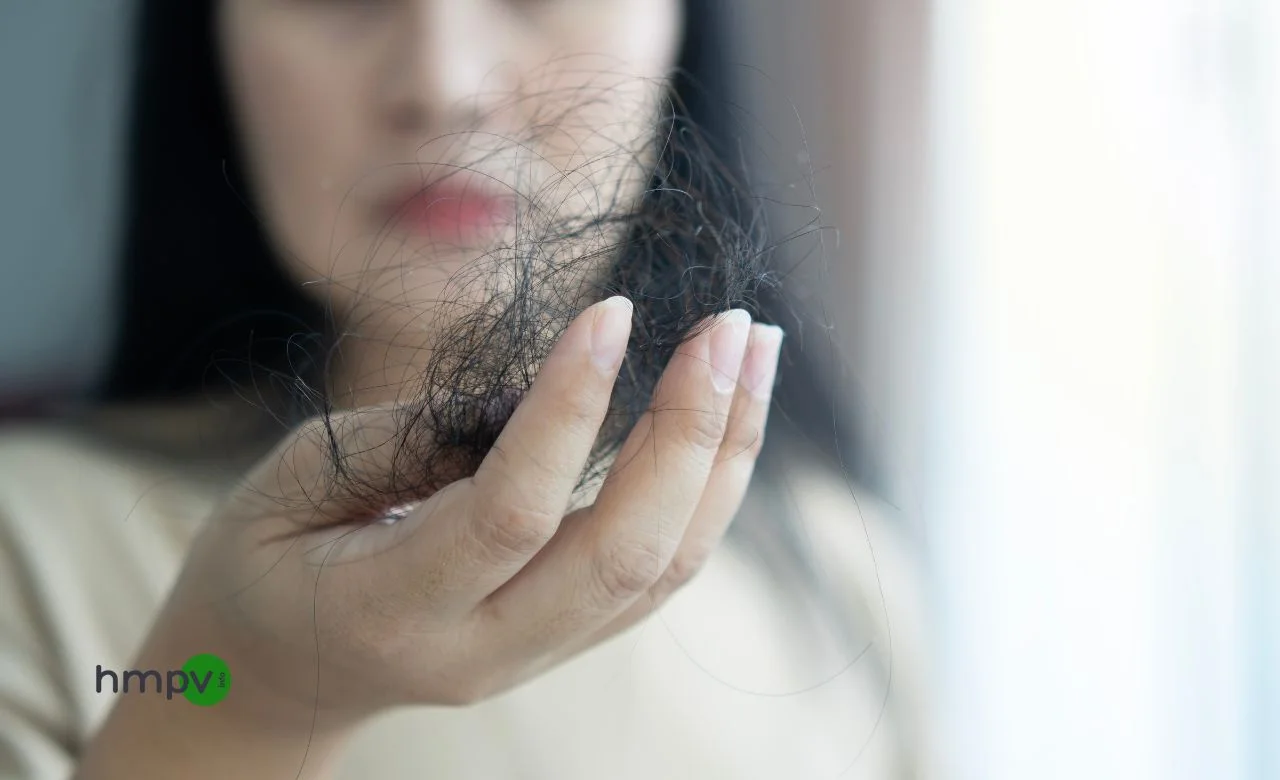
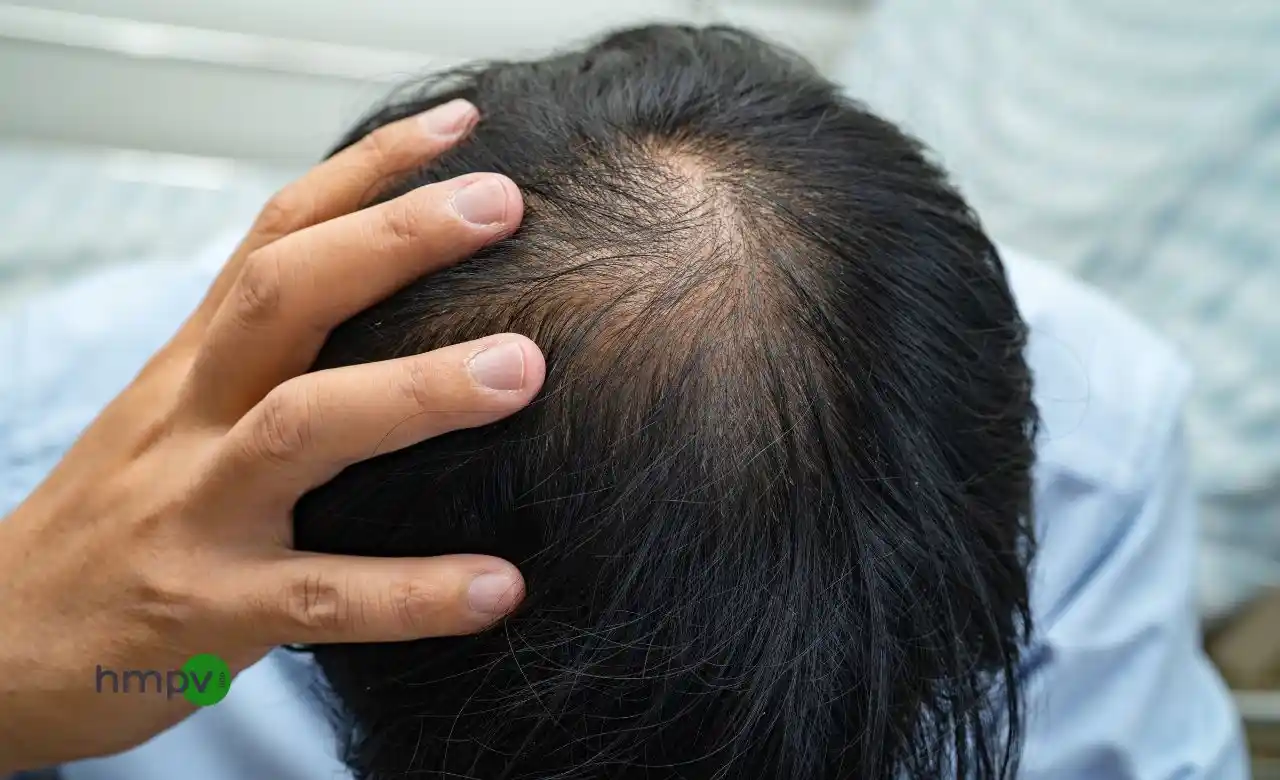
Hair loss. It starts slowly—a little extra hair on your pillow, a receding hairline that wasn’t there before, a thinning crown. And before you know it, your hair just doesn’t look the same. Sound familiar? You’re not alone.
Male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) affects over 50% of men by age 50—and for many, it starts much earlier. Some embrace the bald look. Others fight it. But no matter where you stand, understanding why it happens and what you can do about it is key.
Let’s dive into the causes, stages, and best treatments for male pattern baldness.
Why Does Male Pattern Baldness Happen?
The truth? It’s in your genes.
Male pattern baldness is mostly hereditary, meaning if your dad or grandfather lost their hair, you’re more likely to experience it too. But genetics aren’t the only factor.
Here’s what’s really going on:
- DHT (Dihydrotestosterone) – The Hair Killer
DHT is a hormone that shrinks hair follicles over time. As DHT levels rise, hair grows thinner, weaker, and eventually stops growing altogether. - Age Plays a Role
Hair loss usually starts in your 20s or 30s and becomes more noticeable over time. - Lifestyle Matters
Poor diet, stress, and lack of sleep won’t directly cause baldness, but they can speed up hair thinning.
Bottom line: If you’re genetically prone to hair loss, DHT will do its job. But that doesn’t mean you’re powerless.
The 7 Stages of Male Pattern Baldness
Baldness doesn’t happen overnight. It follows a pattern, known as the Norwood Scale:
Stage 1: No Hair Loss
Your hairline is intact. No thinning yet.
Stage 2: Slight Recession
You might notice a small “M” shape forming at the temples.
Stage 3: Visible Hairline Changes
Your hairline moves back further, making the forehead look bigger.
Stage 4: Thinning at the Crown
The top of your head (crown) starts to thin, along with the hairline recession.
Stage 5: Larger Bald Spot
The bald areas on the crown and front get closer together.
Stage 6: Almost Bald
Only a thin strip of hair remains on the sides and back of your head.
Stage 7: Full Baldness
The horseshoe-shaped hair pattern is all that’s left.
Where do you fall on the scale? The earlier you take action, the better your chances of slowing hair loss.
Best Treatments for Male Pattern Baldness
There’s no miracle cure, but these treatments can help slow or even reverse hair loss.
1. Minoxidil (Rogaine) – The Easy Option
- Available over the counter
- Slows hair loss and promotes regrowth
- Must be used forever to maintain results
2. Finasteride (Propecia) – The DHT Blocker
- Prescription pill that lowers DHT levels
- Can stop hair loss and even regrow hair
- Potential side effects (low sex drive, mood changes)
3. Hair Transplant – Permanent Solution
- Takes hair from the back of your head and transplants it to bald areas
- Looks natural when done right
- Expensive and requires surgery
4. PRP Therapy – Platelet-Rich Plasma
- Uses your own blood to stimulate hair growth
- Safe and natural
- Requires multiple treatments
5. Laser Therapy – Low-Level Light Therapy (LLLT)
- Stimulates hair follicles using light therapy
- Painless and easy to use at home
- Results vary from person to person
6. Lifestyle Fixes – Hair Health from the Inside Out
- Eat more protein, iron, and vitamins (eggs, fish, nuts)
- Reduce stress (yes, stress can speed up hair loss)
- Avoid harsh hairstyles and overwashing your hair
Final Thoughts: Own Your Look, Own Your Confidence
Hair or no hair, you are still you. Some men fight baldness, some rock the shaved look, and both choices are valid. The key is understanding your options and doing what feels right for YOU.
If you want to slow hair loss, start early—the sooner, the better. If you’re ready to embrace baldness, own it with confidence. Either way, your worth isn’t measured by your hairline.















Leave a Reply