Have you ever noticed dark spots or uneven patches of skin and wondered what’s going on? Skin pigmentation disorders, like melasma and hyperpigmentation, are more common than you think. While they’re not harmful to your health, they can affect how you feel about your appearance. But don’t worry! Understanding these skin issues and how to treat them can help you regain control of your skin’s health.
Let’s dive into the world of skin pigmentation disorders and how you can treat them to get back your glowing, even complexion.
What Are Skin Pigmentation Disorders?
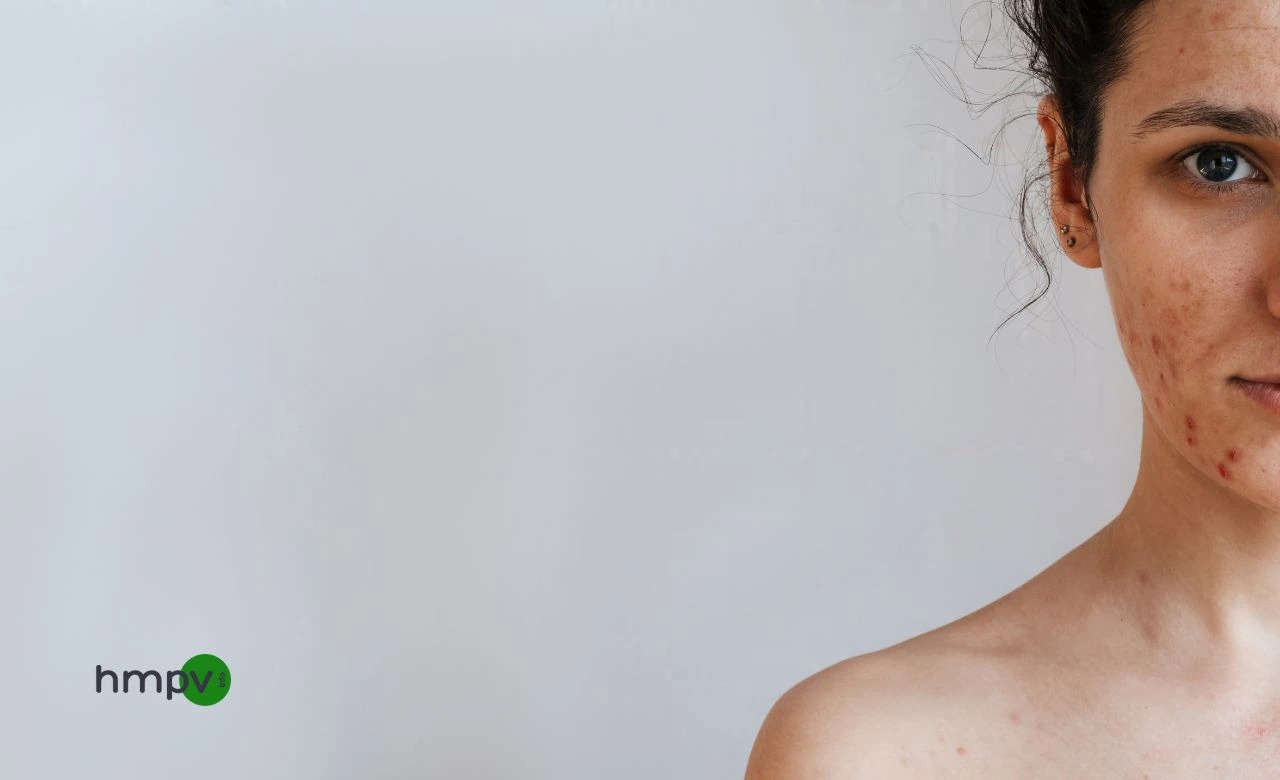
Skin pigmentation disorders occur when the body produces too much or too little melanin, the pigment responsible for your skin color. Melanin helps protect your skin from UV damage, but sometimes it doesn’t work quite as it should. This imbalance leads to dark patches or spots, uneven skin tone, or lighter skin in certain areas.
Common Types of Skin Pigmentation Disorders
1. Melasma
Melasma is a common condition that results in dark, irregular patches, often on the face. It usually affects women, especially during pregnancy (which is why it’s often called the “mask of pregnancy”) or when taking birth control pills. Sun exposure is a major trigger for melasma, making it more noticeable during warmer months.
What to Do:
If you have melasma, avoid sun exposure and always wear sunscreen. Topical treatments, like hydroquinone or retinoids, can help lighten dark spots. Consult with your dermatologist for the best plan.
2. Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation refers to any darkening of the skin. It can be caused by acne scars, cuts, or even sun exposure. These dark spots are often harmless but can cause uneven skin tone. For people with sensitive skin, hyperpigmentation might last longer and be harder to treat.
What to Do:
To prevent hyperpigmentation, wear sunscreen every day. For existing spots, products containing vitamin C or alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) can brighten and even out the skin tone.
3. Age Spots (Liver Spots)
Age spots, or liver spots, are small, flat, brown spots that typically appear on areas of skin that have been exposed to the sun for many years. They usually appear on your face, hands, shoulders, or arms.
What to Do:
While age spots are harmless, you can fade them with topical treatments like brightening serums or chemical peels. Regular sunscreen use helps prevent new spots from forming.
4. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
PIH occurs after your skin has been irritated, inflamed, or injured. For example, if you have a pimple that heals and leaves a dark mark, that’s PIH. This type of pigmentation is common after acne, burns, or other skin conditions.
What to Do:
For PIH, the key is patience. Topical treatments like retinoids, vitamin C, or niacinamide can fade dark spots over time. Again, be sure to protect your skin from the sun.
How to Prevent Skin Pigmentation Disorders
While some factors, like genetics, can’t be controlled, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of pigmentation issues:
-
Always Wear Sunscreen
Protect your skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays, even on cloudy days. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, and reapply it every two hours. -
Avoid Scratching or Picking at Skin
If you have acne or cuts, resist the urge to pick or scratch. This can cause scars or trigger hyperpigmentation that lingers for months. -
Use Gentle Skincare Products
Avoid harsh chemicals that can irritate your skin. Opt for gentle exfoliants and soothing moisturizers to prevent flare-ups. -
Get Regular Skin Check-Ups
See a dermatologist if you notice any changes in your skin color or texture. Early detection of pigmentation disorders can lead to better treatment results.
Treatment Options for Skin Pigmentation Disorders
Treatment will depend on the type and severity of the pigmentation issue. Common options include:
- Topical Treatments: Creams and serums containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, and vitamin C can lighten dark spots and even out skin tone.
- Laser Treatments: For stubborn pigmentation, laser therapy can target and break down excess melanin in the skin.
- Chemical Peels: These can help improve skin tone by removing dead skin cells and encouraging new cell growth.
- Prescription Medications: For more severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe topical or oral treatments to manage pigmentation issues.
Final Thoughts: Embrace Your Skin
Pigmentation disorders might feel frustrating, but remember that your skin is unique and deserves care. There are plenty of treatments and preventative measures to help manage pigmentation issues. With the right approach, you can restore your skin’s natural balance and feel confident in your complexion again.
If you’re struggling with skin pigmentation, don’t hesitate to consult a dermatologist. With patience, the right products, and sun protection, you can bring out the natural beauty of your skin.













Leave a Reply